Introduction
Welcome to this series of blog posts where I will be documenting my journey of setting up a home server using Kubernetes and NGINX Ingress Controller. This is the first part of the series where I will be setting up the networking for the home server.
I have chosen to use k0s as the Kubernetes distribution for this project. k0s allows me to set up a multi-node (or single node) Kubernetes cluster by specifying the IP addresses of the nodes in the k0sctl.yaml file. I will also be using MetalLB which allow creation of Services of type LoadBalaner on the cluster. More specifically, it will allows the NGINX Ingress Controller service to have an external IP address, otherwise this will show up as pending.
Installing the Operating System
The first step is to install an operating system on the servers that will be used as part of the cluster. I have installed Ubuntu 23.10 on my two nodes. One is a Raspberry Pi 4 (with 4GB of ram) and the other is a Beelink SER7 7840HS with 32 GB of ram.
The current supported operating systems and architectures for k0s nodes are listed here.
After installing your operating system, make sure to connect the nodes to the same network and give them static IP addresses. You can lock the IP addresses to the MAC addresses of the nodes in your router settings.
It is also important to give the nodes a unique hostname. You can do this by editing the /etc/hostname file. I have named my SER7 node hendrix and my Raspberry Pi 4 node rpi.
Setting up SSH
In order for k0sctl to work, it needs to be able to SSH into the nodes as the root user. From your primary machine (which should also be on the same network), copy your SSH public key to the nodes. You can do this by running the following command:
ssh-copy-id root@<node-ip>Do this for each node you have in your cluster. You should now be able to SSH into the nodes without needing to enter a password.
ssh root@<node-ip>Installing k0s on the Nodes
k0s has a tool called k0sctl which is used to install and manage the k0s cluster. You can download this tool on your primary machine (outside the cluster) using the instructions in its GitHub repository.
Now, create a k0sctl.yaml file with the following content:
apiVersion: k0sctl.k0sproject.io/v1beta1
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: k0s-cluster
spec:
hosts:
- ssh:
address: 192.168.1.160
user: root
port: 22
keyPath: ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
role: controller+worker
- ssh:
address: 192.168.1.106
user: root
port: 22
keyPath: ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
role: worker
k0s:
version: ""
config:
spec:
extensions:
helm:
repositories:
- name: metallb
url: https://metallb.github.io/metallb
charts:
- name: metallb
chartname: metallb/metallb
namespace: metallb-systemReplace the address field with the IP addresses of your nodes. The role field specifies the role of the node. In this case, the first node is both a controller and a worker, and the second node is just a worker. k0s has a helm extension which allows you to install helm charts on the cluster. Here, I am installing the MetalLB helm chart to the cluster via k0sctl.
Now, run the following command to install the k0s cluster:
k0sctl apply --config k0sctl.yamlAfter running this command, you should see the k0s cluster being installed on your nodes.
Using your KubeConfig
k0sctl kubeconfig will generate a kubeconfig file for you to use to interact with the cluster. You can then interact with the cluster using kubectl.
The easiest way to do this is to copy the kubeconfig file to ~/.kube/config on your primary machine, with the following command:
k0sctl kubeconfig > ~/.kube/configYou can now interact with the cluster using kubectl:
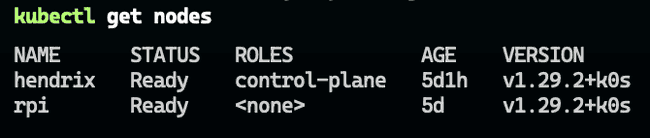
kubectl get nodesApplying the MetalLB Config
The last step before installing the NGINX Ingress Controller is to apply the MetalLB configuration. This will allow the NGINX Ingress Controller service to have an external IP address.
Before applying the MetalLB configuration, you need to decide on a range of IP addresses that MetalLB can use. This range should be within the IP address range of your network. I have chosen the range 192.168.1.180-192.168.1.199. Ensure that these IP addresses that you choose are not already in use on your network.
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: IPAddressPool
metadata:
name: my-ip-pool
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
addresses:
- 192.168.1.180-192.168.1.199
---
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: L2Advertisement
metadata:
name: my-l2advertisement
namespace: metallb-systemApply the MetalLB configuration using the following command:
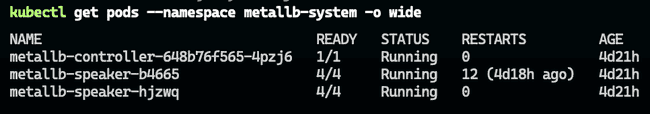
kubectl apply -f metallb-config.yamlNow, you should be able to see the MetalLB pods running in the metallb-system namespace:
kubectl get pods --namespace metallb-systemInstalling the NGINX Ingress Controller
Now that we have MetalLB installed, we can install NGINX Ingress Controller. The default installation of NGINX Ingress Controller via helm uses a LoadBalancer service type, which is why we needed to install MetalLB first.
Adding the NGINX Helm Repository
helm repo add nginx-stable https://helm.nginx.com/stable
helm repo updateAs we are going to be modifying the default helm chart, we need to first download the helm chart to our local machine. You can do this by running the following command:
helm pull nginx-stable/nginx-ingress --untarModifying the Helm Chart
I need to add a toleration under the controller section of the values.yaml file. This is because NGINX Ingress Controller could end up on my controller+worker node that I defined in k0sctl.yaml.
controller:
tolerations:
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"Installing the NGINX Ingress Controller helm chart
helm install nginx-ingress ./nginx-ingress --namespace nginx-ingress --create-namespaceNow NGINX Ingress Controller should be installed on your cluster.
You can check the status of the NGINX Ingress Controller pods by running the following command:
kubectl get pods --namespace nginx-ingressTo get the externalIP address of the NGINX Ingress Controller LoadBalancer service, run the following command:
kubectl get svc --namespace nginx-ingressYou should now be able to access the NGINX Ingress Controller using the externalIP address. This will show a default 404 page.
curl -I <externalIP>Exposing NGINX Ingress Controller to the Internet
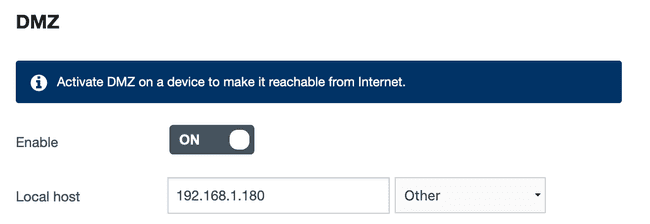
The last step is to expose the NGINX Ingress Controller to the internet. This can be done by setting up port forwarding on your router. You will need to forward ports 80 and 443 to the externalIP address of the NGINX Ingress Controller LoadBalancer service, or use the externalIP address as the DMZ host.
After this, you should be able to access the NGINX Ingress Controller from the internet, via your public IP address.
Conclusion
In this part, I have set up the networking for the home server. I have installed k0s on the nodes, set up MetalLB to allow the NGINX Ingress Controller service to have an external IP address, and installed the NGINX Ingress Controller. In the next part, I will be setting up the external-dns and cert-manager.